Dynamic infrastructures
Opposing to well-established deployments with an almost-static set of computing resources and hardly-varying interconnection conditions such as a single-computer, a cluster or a supercomputer; dynamic infrastructures, like Fog environments, require a different kind of deployment able to adapt to rapidly-changing conditions. Such infrastructures are likely to comprise several mobile devices whose connectivity to the infrastructure is temporary. When the device is within the network range, it joins an already existing COMPSs deployment and interacts with the other resources to offload tasks onto them or viceversa. Eventually, the connectivity of that mobile device could be disrupted to never reestablish. If the leaving device was used as a worker node, the COMPSs master needs to react to the departure and reassign the tasks running on that node. If the device was the master node, it should be able to carry on with the computation being isolated from the rest of the infrastructure or with another set of available resources.
What are COMPSs Agents?
COMPSs Agents is a deployment approach especially designed to fit in this kind of environments. Each device is an autonomous individual with processing capabilities hosting the execution of a COMPSs runtime as a background service. Applications - running on that device or on another - can contact this service to request the execution of a function in a serverless, stateless manner (resembling the Function-as-a-Service model). If the requested function follows the COMPSs programming model, the runtime will parallelise its execution as if it were the main function of a regular COMPSs application.
Agents can associate with other agents by offering their embedded computing resources to execute functions to achieve a greater purpose; in exchange, they receive a platform where they can offload their computation in the same manner, and, thus, achieve lower response times. As opossed to the master-worker approach followed by the classic COMPSs deployment, where a single node produces the all the workload, in COMPSs Agents deployments, any of the nodes within the platform becomes a potential source of computation to distribute. Therefore, this master-centric approach where workload producer to orchestrate holistically the execution is no longer valid. Besides, concentrating all the knowledge of several applications and handling the changes of infrastructure represents an important computational burden for the resource assuming the master role, especially if it is a resource-scarce device like a mobile. For this two reasons, COMPSs agents proposes a hierachic approach to organize the nodes. Each node will only be aware of some devices with which it has direct connection and only decides whether the task runs on its embedded computing devices or if the responsability of executing the task is delegated onto one of the other agents. In the latter case, the receiver node will face the same problem and decide whether it should host the execution or forward it to a different node.
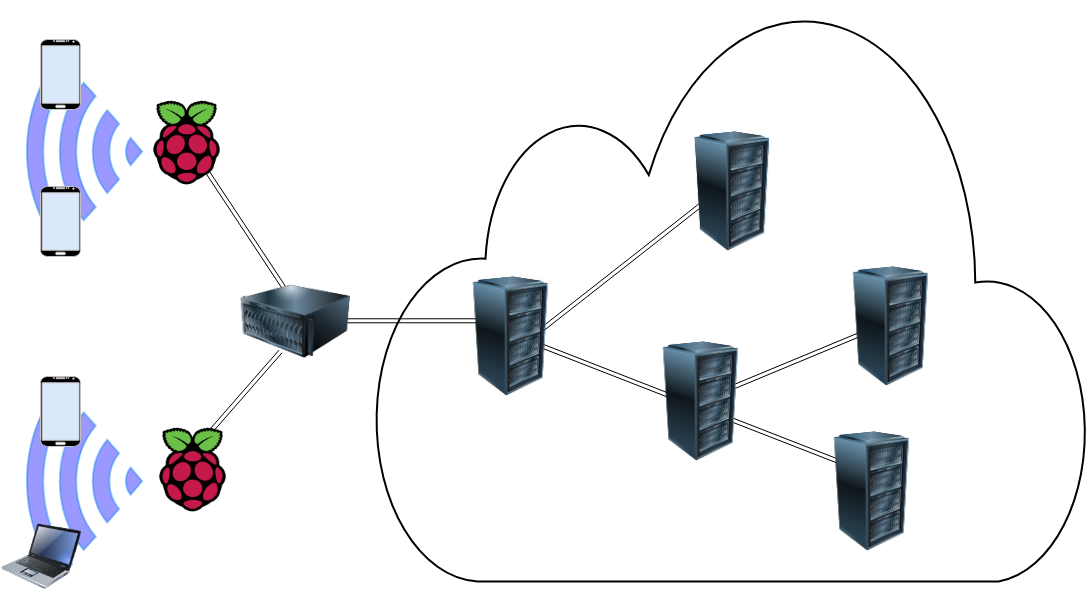
The following image illustrates an example of a COMPSs agents hierarchy that could be deployed in any kind of facilities; for instance, a university campus. In this case, students only interact directly with their mobile phones and laptops to run their applications; however, the computing workload produced by them is distributed across the whole system. To do so, the mobile devices need to connect to one of the edge devices devices scattered across the facilities acting as a Wi-Fi Hotspot (in the example, raspberry Pi) which runs a COMPSs agent. To submit the operation execution to the platform, mobile devices can either contact a COMPSs agent running in the device or the application can directly contact the remote agent running on the rPI. All rPi agents are connected to an on-premise server within the campus that also runs a COMPSs Agent. Upon an operation request by a user device, the rPi can host the computation on its own devices or forward the request to one of its neighbouring agents: the on-premise server or another user’s device running a COMPSs agent. In the case that the rPi decides to move up the request through the hierarchy, the on-premise server faces a similar problem: hosting the computation on its local devices, delegating the execution onto one of the rPi – which in turn could forward the execution back to another user’s device –, or submit the request to a cloud. Internally, the Cloud can also be organized with COMPSs Agents hierarchy; thus, one of its nodes can act as the gateway to receive external requests and share the workload across the whole system.
Deploying a COMPSs Agent
COMPSs Agents are deployed using the compss_agent_start command:
compss@bsc:~$ compss_agent_start [OPTION]
There is one mandatory parameter --hostname that indicates the name that other agents and itself use to refer to the agent. Bear in mind that agents are not able to dynamically modify its classpath; therefore, the --classpath parameter becomes important to indicate the application available on the agent. Any public method available on the classpath is an execution request candidate.
The following command raises an agent with name 192.168.1.100 and any of the public methods of the classes encapsulated in the jarfile /app/path.jar can be executed.
compss@bsc:~$ compss_agent_start --hostname=192.168.1.100 --classpath=/app/path.jar
The compss_agent_start command allows users to set up the COMPSs runtime by specifyng different options in the same way as done for the runcompss command. To indicate the available resources, the device administrator can use the --project and --resources option exactly in the same way as for the runcompss command. For further details on how to dynamically modify the available resources, please, refer to section Modifying the available resources.
Currently, COMPSs agents allow interaction through two interfaces: the Comm interface and the REST interface. The Comm interface leverages on a propietary protocol to submit operations and request updates on the current resource configuration of the agent. Although users and applications can use this interface, its design purpose is to enable high-performance interactions among agents rather than supporting user interaction. The REST interface takes the completely opposed approach; Users should interact with COMPSs agents through it rather than submitting tasks with the Comm interface. The COMPSs agent allows to enact both interfaces at a time; thus, users can manually submit operations using the REST interface, while other agents can use the Comm interface. However, the device owner can decide at deploy time which of the interfaces will be available on the agent and through which port the API will be exposed using the rest_port and comm_port options of the compss_agent_start command. Other agents can be configured to interact with the agent through any of the interfaces. For further details on how to configure the interaction with another agent, please, refer to section Modifying the available resources.
compss@bsc:~$ compss_agent_start -h
Usage: /opt/COMPSs/Runtime/scripts/user/compss_agent_start [OPTION]...
COMPSs options:
--appdir=<path> Path for the application class folder.
Default: /home/flordan/git/compss/framework/builders
--classpath=<path> Path for the application classes / modules
Default: Working Directory
--comm=<className> Class that implements the adaptor for communications with other nodes
Supported adaptors:
├── es.bsc.compss.nio.master.NIOAdaptor
├── es.bsc.compss.gat.master.GATAdaptor
├── es.bsc.compss.agent.rest.Adaptor
└── es.bsc.compss.agent.comm.CommAgentAdaptor
Default: es.bsc.compss.agent.comm.CommAgentAdaptor
--comm_port=<int> Port on which the agent sets up a Comm interface. (<=0: Disabled)
-d, --debug Enable debug. (Default: disabled)
--hostname Name with which itself and other agents will identify the agent.
--library_path=<path> Non-standard directories to search for libraries (e.g. Java JVM library, Python library, C binding library)
Default: Working Directory
--log_dir=<path> Log directory. (Default: /tmp/)
--log_level=<level> Set the debug level: off | info | api | debug | trace
Default: off
--master_port=<int> Port to run the COMPSs master communications.
(Only when es.bsc.compss.nio.master.NIOAdaptor is used. The value is overriden by the comm_port value.)
Default: [43000,44000]
--pythonpath=<path> Additional folders or paths to add to the PYTHONPATH
Default: /home/flordan/git/compss/framework/builders
--project=<path> Path of the project file
(Default: /opt/COMPSs/Runtime/configuration/xml/projects/examples/local/project.xml)
--resources=<path> Path of the resources file
(Default: /opt/COMPSs/Runtime/configuration/xml/resources/examples/local/resources.xml)
--rest_port=<int> Port on which the agent sets up a REST interface. (<=0: Disabled)
--scheduler=<className> Class that implements the Scheduler for COMPSs
Supported schedulers:
├── es.bsc.compss.scheduler.data.DataScheduler
├── es.bsc.compss.scheduler.fifo.FIFOScheduler
├── es.bsc.compss.scheduler.fifodata.FIFODataScheduler
├── es.bsc.compss.scheduler.lifo.LIFOScheduler
├── es.bsc.compss.components.impl.TaskScheduler
└── es.bsc.compss.scheduler.loadbalancing.LoadBalancingScheduler
Default: es.bsc.compss.scheduler.loadbalancing.LoadBalancingScheduler
--scheduler_config_file=<path> Path to the file which contains the scheduler configuration.
Default: Empty
--summary Displays a task execution summary at the end of the application execution
Default: false
Other options:
--help prints this message
Executing an operation
The compss_agent_call_operation commands interacts with the REST interface of the COMPSs agent to submit an operation.
compss@bsc:~$ compss_agent_call_operation [options] application_name application_arguments
The command has two mandatory flags --master_node and --master_port to indicate the endpoint of the COMPSs Agent. By default, the command submits an execution of the main method of the Java class with the name passed in as the application_name and gathering all the application arguments in a single String[] instance. To execute Python methods, the user can use the --lang=PYTHON option and the Agent will execute the python script with the name passed in as application_name. Operation invocations can be customized by using other options of the command. The --method_name option allow to execute a specific method; in the case of specifying a method, each of the parameters will be passed in as a different parameter to the function and it is necessary to indicate the --array flag to encapsulate all the parameters as an array.
compss@bsc.es:~$ compss_agent_call_operation -h
Usage: compss_agent_call_operation [options] application_name application_arguments
* Options:
General:
--help, -h Print this help message
--opts Show available options
--version, -v Print COMPSs version
--master_node=<string> Node where to run the COMPSs Master
Mandatory
--master_port=<string> Node where to run the COMPSs Master
Mandatory
Launch configuration:
--cei=<string> Canonical name of the interface declaring the methods
Default: No interface declared
--lang=<string> Language implementing the operation
Default: JAVA
--method_name=<string> Name of the method to invoke
Default: main and enables array parameter
--parameters_array, --array Parameters are encapsulated as an array
Default: disabled
For example, to submit the execution of the demoFunction method from the es.bsc.compss.tests.DemoClass class passing in a single parameter with value 1 on the agent 127.0.0.1 with a REST interface listening on port 46101, the user should execute the following example command:
compss@bsc.es:~$ compss_agent_call_operation --master_node="127.0.0.1" --master_port="46101" --method_name="demoFunction" es.bsc.compss.test.DemoClass 1
For the agent to detect inner tasks within the operation execution, the COMPSs Programming model requires an interface selecting the methods to be replaced by asyncrhonous task creations. An invoker should use the --cei option to specify the name of the interface selecting the tasks.
Modifying the available resources
Finally, the COMPSs framework offers tree commands to control dynamically the pool of resources available for the runtime un one agent. These commands are compss_agent_add_resources, compss_agent_reduce_resources and compss_agent_lost_resources.
The compss_agent_add_resources commands interacts with the REST interface of the COMPSs agent to attach new resources to the Agent.
compss@bsc.es:~$ compss_agent_add_resources [options] resource_name [<adaptor_property_name=adaptor_property_value>]
By default, the command modifies the resource pool of the agent deployed on the node running the command listenning on port 46101; however, this can be modified by using the options --agent_node and --agent_port to indicate the endpoint of the COMPSs Agent. The other options passed in to the command modify the characteristics of the resources to attach; by default, it adds one single CPU core. However, it also allows to modify the amount of GPU cores, FPGAs, memory type and size and OS details.
compss@bsc.es:~$ compss_agent_add_resources -h
Usage: compss_agent_add_resources [options] resource_name [<adaptor_property_name=adaptor_property_value>]
* Options:
General:
--help, -h Print this help message
--opts Show available options
--version, -v Print COMPSs version
--agent_node=<string> Name of the node where to add the resource
Default:
--agent_port=<string> Port of the node where to add the resource
Default:
Resource description:
--comm=<string> Canonical class name of the adaptor to interact with the resource
Default: es.bsc.compss.agent.comm.CommAgentAdaptor
--cpu=<integer> Number of cpu cores available on the resource
Default: 1
--gpu=<integer> Number of gpus devices available on the resource
Default: 0
--fpga=<integer> Number of fpga devices available on the resource
Default: 0
--mem_type=<string> Type of memory used by the resource
Default: [unassigned]
--mem_size=<string> Size of the memory available on the resource
Default: -1
--os_type=<string> Type of operating system managing the resource
Default: [unassigned]
--os_distr=<string> Distribution of the operating system managing the resource
Default: [unassigned]
--os_version=<string> Version of the operating system managing the resource
Default: [unassigned]
If resource_name matches the name of the Agent, the capabilities of the device are increased according to the description; otherwise, the runtime adds a remote worker to the resource pool with the specified characteristics. Notice that, if there is another resource within the pool with the same name, the agent will increase the resources of such node instead of adding it as a new one. The --comm option is used for selecting which adaptor is used for interacting with the remote node; the default adaptor (CommAgent) interacts with the remote node through the Comm interface of the COMPSs agent.
The following command adds a new Agent onto the pool of resources of the Agent deployed at IP 192.168.1.70 with a REST Interface on port 46101. The new agent, which has 4 CPU cores, is deployed on IP 192.168.1.72 and has a Comm interface endpoint on port 46102.
compss@bsc.es:~$ compss_agent_add_resources --agent_node=192.168.1.70 --agent_port=46101 --cpu=4 192.168.1.72 Port=46102
Conversely, the compss_agent_reduce_resources command allows to reduce the number of resources configured in an agent. Executing the command causes the target agent to reduce the specified amount of resources from one of its configured neighbors. At the moment the reception of the resource removal request, the agent might be using actively using those remote resources by executing some tasks. If that is the case, the agent will register the resource reduction request, stop submitting more workload to the corresponding node, and, when the idle resources of the node match the request, the agent removes them from the pool. If upon the completion of the compss_agent_reduce_resources command no resources are associated to the reduced node, the node is completely removed from the resource pool of the agent. The options and default values are the same than for the compss_agent_add_resources command. Notice that --comm option is not available because only one resource can associated to that name regardless the selected adaptor.
compss@bsc.es:~$ compss_agent_reduce_resources -h
Usage: compss_agent_reduce_resources [options] resource_name
* Options:
General:
--help, -h Print this help message
--opts Show available options
--version, -v Print COMPSs version
--agent_node=<string> Name of the node where to add the resource
Default:
--agent_port=<string> Port of the node where to add the resource
Default:
Resource description:
--cpu=<integer> Number of cpu cores available on the resource
Default: 1
--gpu=<integer> Number of gpus devices available on the resource
Default: 0
--fpga=<integer> Number of fpga devices available on the resource
Default: 0
--mem_type=<string> Type of memory used by the resource
Default: [unassigned]
--mem_size=<string> Size of the memory available on the resource
Default: -1
--os_type=<string> Type of operating system managing the resource
Default: [unassigned]
--os_distr=<string> Distribution of the operating system managing the resource
Default: [unassigned]
--os_version=<string> Version of the operating system managing the resource
Default: [unassigned]
Finally, the last command to control the pool of resources configured, compss_agent_lost_resources, immediately removes from an agent’s pool all the resources corresponding to the remote node associated to that name.
compss@bsc.es:~$ compss_agent_lost_resources [options] resource_name
In this case, the only available options are those used for identifying the endpoint of the agent:--agent_node and --agent_port. As with the previous commands, by default, the request is submitted to the agent deployed on the IP address 127.0.0.1 and listenning on port 46101.