Matmul
The matmul performs the matrix multiplication of two matrices.
import time
import numpy as np
from pycompss.api.task import task
from pycompss.api.parameter import INOUT
from pycompss.api.api import compss_barrier
from pycompss.api.api import compss_wait_on
@task(returns=1)
def generate_block(size, num_blocks, seed=0, set_to_zero=False):
"""
Generate a square block of given size.
:param size: <Integer> Block size
:param num_blocks: <Integer> Number of blocks
:param seed: <Integer> Random seed
:param set_to_zero: <Boolean> Set block to zeros
:return: Block
"""
np.random.seed(seed)
if not set_to_zero:
b = np.random.random((size, size))
# Normalize matrix to ensure more numerical precision
b /= np.sum(b) * float(num_blocks)
else:
b = np.zeros((size, size))
return b
@task(C=INOUT)
def fused_multiply_add(A, B, C):
"""
Multiplies two Blocks and accumulates the result in an INOUT Block (FMA).
:param A: Block A
:param B: Block B
:param C: Result Block
:return: None
"""
C += np.dot(A, B)
def dot(A, B, C):
"""
A COMPSs blocked matmul algorithm.
:param A: Block A
:param B: Block B
:param C: Result Block
:return: None
"""
n, m = len(A), len(B[0])
# as many rows as A, as many columns as B
for i in range(n):
for j in range(m):
for k in range(n):
fused_multiply_add(A[i][k], B[k][j], C[i][j])
def main(num_blocks, elems_per_block, seed):
"""
Matmul main.
:param num_blocks: <Integer> Number of blocks
:param elems_per_block: <Integer> Number of elements per block
:param seed: <Integer> Random seed
:return: None
"""
start_time = time.time()
# Generate the dataset in a distributed manner
# i.e: avoid having the master a whole matrix
A, B, C = [], [], []
matrix_name = ["A", "B"]
for i in range(num_blocks):
for l in [A, B, C]:
l.append([])
# Keep track of blockId to initialize with different random seeds
bid = 0
for j in range(num_blocks):
for ix, l in enumerate([A, B]):
l[-1].append(generate_block(elems_per_block,
num_blocks,
seed=seed + bid))
bid += 1
C[-1].append(generate_block(elems_per_block,
num_blocks,
set_to_zero=True))
compss_barrier()
initialization_time = time.time()
# Do matrix multiplication
dot(A, B, C)
compss_barrier()
multiplication_time = time.time()
print("-----------------------------------------")
print("-------------- RESULTS ------------------")
print("-----------------------------------------")
print("Initialization time: %f" % (initialization_time -
start_time))
print("Multiplication time: %f" % (multiplication_time -
initialization_time))
print("Total time: %f" % (multiplication_time - start_time))
print("-----------------------------------------")
def parse_args():
"""
Arguments parser.
Code for experimental purposes.
:return: Parsed arguments.
"""
import argparse
description = 'COMPSs blocked matmul implementation'
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description=description)
parser.add_argument('-b', '--num_blocks', type=int, default=1,
help='Number of blocks (N in NxN)'
)
parser.add_argument('-e', '--elems_per_block', type=int, default=2,
help='Elements per block (N in NxN)'
)
parser.add_argument('--seed', type=int, default=0,
help='Pseudo-Random seed'
)
return parser.parse_args()
if __name__ == "__main__":
opts = parse_args()
main(**vars(opts))
The matrix multiplication application can be executed by invoking the
runcompss command with the desired parameters (in this case we use -g
to generate the task depedency graph) and application.
The following lines provide an example of its execution considering 4 x 4 Blocks
of 1024 x 1024 elements each block, which conforms matrices of 4096 x 4096 elements.
compss@bsc:~$ runcompss -g matmul.py -b 4 -e 1024
[ INFO] Inferred PYTHON language
[ INFO] Using default location for project file: /opt/COMPSs//Runtime/configuration/xml/projects/default_project.xml
[ INFO] Using default location for resources file: /opt/COMPSs//Runtime/configuration/xml/resources/default_resources.xml
[ INFO] Using default execution type: compss
----------------- Executing matmul.py --------------------------
WARNING: COMPSs Properties file is null. Setting default values
[(439) API] - Starting COMPSs Runtime v2.7 (build 20200519-1005.r6093e5ac94d67250e097a6fad9d3ec00d676fe6c)
-----------------------------------------
-------------- RESULTS ------------------
-----------------------------------------
Initialization time: 4.112615
Multiplication time: 2.366103
Total time: 6.478717
-----------------------------------------
[(5609) API] - Execution Finished
------------------------------------------------------------
Figure 48 depicts the generated task dependency graph. The dataset generation can be identified in the blue tasks, while the white tasks represent the multiplication of a block with another.
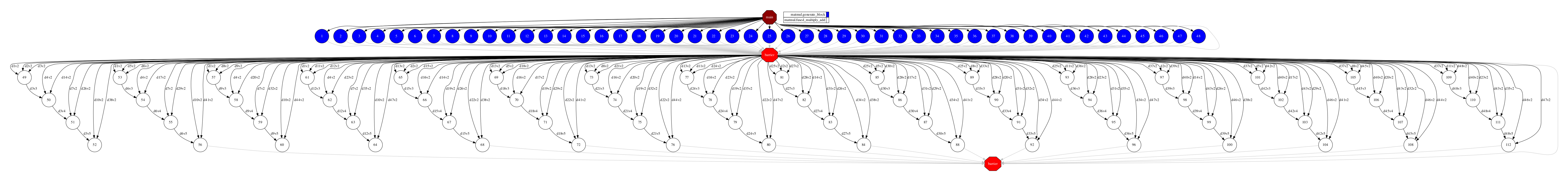
Figure 48 Python matrix multiplication tasks graph