1.13. Machine Learning with dislib
This tutorial will show the different algorithms available in dislib.
Setup
First, we need to start an interactive PyCOMPSs session:
[1]:
import pycompss.interactive as ipycompss
import os
if 'BINDER_SERVICE_HOST' in os.environ:
ipycompss.start(graph=True,
project_xml='../xml/project.xml',
resources_xml='../xml/resources.xml')
else:
ipycompss.start(graph=True, monitor=1000)
******************************************************
*************** PyCOMPSs Interactive *****************
******************************************************
* .-~~-.--. _____ ________ *
* : ) |____ \ |____ / *
* .~ ~ -.\ /.- ~~ . ___) | / / *
* > `. .' < / ___/ / / *
* ( .- -. ) | |___ _ / / *
* `- -.-~ `- -' ~-.- -' |_____| |_| /__/ *
* ( : ) _ _ .-: *
* ~--. : .--~ .-~ .-~ } *
* ~-.-^-.-~ \_ .~ .-~ .~ *
* \ \ ' \ '_ _ -~ *
* \`.\`. // *
* . - ~ ~-.__\`.\`-.// *
* .-~ . - ~ }~ ~ ~-.~-. *
* .' .-~ .-~ :/~-.~-./: *
* /_~_ _ . - ~ ~-.~-._ *
* ~-.< *
******************************************************
* - Starting COMPSs runtime... *
* - Log path : /home/user/.COMPSs/Interactive_01/
* - PyCOMPSs Runtime started... Have fun! *
******************************************************
Next, we import dislib and we are all set to start working!
[2]:
import dislib as ds
Load the MNIST dataset
[3]:
x, y = ds.load_svmlight_file('/tmp/mnist/mnist', # Download the dataset
block_size=(10000, 784), n_features=784, store_sparse=False)
[4]:
x.shape
[4]:
(60000, 784)
[5]:
y.shape
[5]:
(60000, 1)
[6]:
y_array = y.collect()
y_array
[6]:
array([5., 0., 4., ..., 5., 6., 8.])
[7]:
img = x[0].collect().reshape(28,28)
[8]:
%matplotlib inline
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.imshow(img)
[8]:
<matplotlib.image.AxesImage at 0x7f6fab182fd0>

[9]:
int(y[0].collect())
[9]:
5
dislib algorithms
Preprocessing
[10]:
from dislib.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from dislib.decomposition import PCA
Clustering
[11]:
from dislib.cluster import KMeans
from dislib.cluster import DBSCAN
from dislib.cluster import GaussianMixture
Classification
[12]:
from dislib.classification import CascadeSVM
from dislib.classification import RandomForestClassifier
Recommendation
[13]:
from dislib.recommendation import ALS
Model selection
[14]:
from dislib.model_selection import GridSearchCV
Others
[15]:
from dislib.regression import LinearRegression
from dislib.neighbors import NearestNeighbors
Examples
KMeans
[16]:
kmeans = KMeans(n_clusters=10)
pred_clusters = kmeans.fit_predict(x).collect()
Get the number of images of each class in the cluster 0:
[17]:
from collections import Counter
Counter(y_array[pred_clusters==0])
[17]:
Counter({2.0: 4006,
6.0: 244,
3.0: 148,
4.0: 20,
8.0: 36,
1.0: 14,
7.0: 22,
9.0: 16,
0.0: 9,
5.0: 7})
GaussianMixture
Fit the GaussianMixture with the painted pixels of a single image:
[18]:
import numpy as np
img_filtered_pixels = np.stack([np.array([i, j]) for i in range(28) for j in range(28) if img[i,j] > 10])
img_pixels = ds.array(img_filtered_pixels, block_size=(50,2))
gm = GaussianMixture(n_components=7, random_state=0)
gm.fit(img_pixels)
Get the parameters that define the Gaussian components:
[19]:
from pycompss.api.api import compss_wait_on
means = compss_wait_on(gm.means_)
covariances = compss_wait_on(gm.covariances_)
weights = compss_wait_on(gm.weights_)
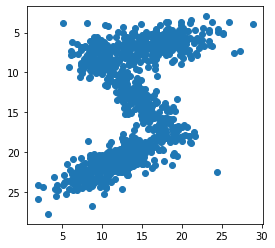
Use the Gaussian mixture model to sample random pixels replicating the original distribution:
[20]:
samples = np.concatenate([np.random.multivariate_normal(means[i], covariances[i], int(weights[i]*1000))
for i in range(7)])
plt.scatter(samples[:,1], samples[:,0])
plt.gca().set_aspect('equal', adjustable='box')
plt.gca().invert_yaxis()
plt.draw()
PCA
[21]:
pca = PCA()
pca.fit(x)
[21]:
PCA(arity=50, n_components=None)
Calculate the explained variance of the 10 first eigenvectors:
[22]:
sum(pca.explained_variance_[0:10])/sum(pca.explained_variance_)
[22]:
0.48814980354934007
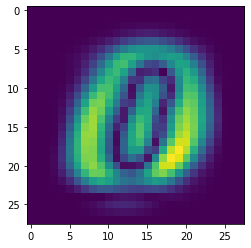
Show the weights of the first eigenvector:
[23]:
plt.imshow(np.abs(pca.components_[0]).reshape(28,28))
[23]:
<matplotlib.image.AxesImage at 0x7f6f9dd987f0>
RandomForestClassifier
[24]:
rf = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=5, max_depth=3)
rf.fit(x, y)
[24]:
RandomForestClassifier(distr_depth='auto', hard_vote=False, max_depth=3,
n_estimators=5, random_state=None,
sklearn_max=100000000.0, try_features='sqrt')
Use the test dataset to get an accuracy score:
[25]:
x_test, y_test = ds.load_svmlight_file('/tmp/mnist/mnist.test', block_size=(10000, 784), n_features=784, store_sparse=False)
score = rf.score(x_test, y_test)
print(compss_wait_on(score))
0.6359
Close the session
To finish the session, we need to stop PyCOMPSs:
[26]:
ipycompss.stop()
****************************************************
*************** STOPPING PyCOMPSs ******************
****************************************************
Warning: some of the variables used with PyCOMPSs may
have not been brought to the master.
****************************************************